Introduction
In the realm of digital data communications, terms like baud rate and bit rate are frequently encountered. These concepts are pivotal in assessing the effectiveness and functionality of communication systems. This article delves into the definition, distinction between baud rate and bit rate, calculation methods, and the importance of baud rate in modern communication systems.
What is Baud Rate?
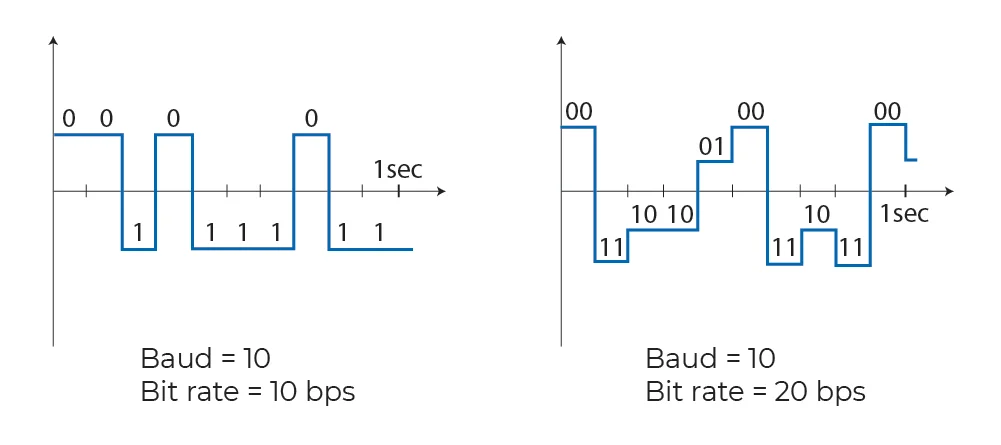
Baud rate signifies the speed at which data is transferred within a communication channel. It quantifies the number of signal changes, such as voltage shifts or pulses, per second, and is typically denoted as “baud” or “Bd.” Essentially, it measures how many times the signal alters its state in a second.
Baud Rate vs. Bit Rate
While baud rate calculates the number of signal changes per second, bit rate, or bits per second (bps), measures the number of bits transmitted per second. In many binary-coded digital systems, 1 Baud equals 1 bps. However, in certain scenarios, one signal change might signify more than one bit, resulting in a higher bps than the baud rate.
Calculating Baud Rate
The baud rate can be computed using the bit rate and the number of bits per data unit. The formula is:
[latex] text{Baud Rate} = frac{text{Bit rate (bps)}}{text{Number of bits per unit data}} [/latex]
For instance, a system with a data rate of 2400 bps, where each signal carries two bits of information, would have a baud rate of 1200 baud.
Baud rate is a fundamental concept in digital communication, and it can be described and understood through various mathematical formulas and relationships. Here are some key formulas related to baud rate:
Baud rate is a fundamental concept in digital communication, and it can be described and understood through various mathematical formulas and relationships. Here are some key formulas related to baud rate:
1. Baud Rate Definition: Baud rate is the number of signal units transmitted per second. It’s given by:
[latex]Baud Rate=frac{1}{Time for one signal unit ( s)}[/latex]
2. Relationship with Bit Rate: If each signal unit represents [latex] n [/latex] bits, then the bit rate [latex] R [/latex] is related to the baud rate [latex] B [/latex] as:
[latex]R = B times n[/latex]
3. Nyquist Formula: The Nyquist formula gives the maximum data rate for a given bandwidth [latex] BW[/latex]:
[latex]R=2times BWtimes log _2left(Lright)[/latex]
where [latex] L [/latex] is the number of signal levels.
4. Shannon Capacity Formula: The Shannon Capacity formula gives the maximum possible data rate for a given bandwidth [latex]BW [/latex] and signal-to-noise ratio [latex]SNR [/latex]:
[latex]C=BWtimes log _2left(1+SNRright) [/latex]
This can be used to understand the limitations of a communication channel and choose an appropriate baud rate.
5. Calculating Time for Transmission: The total time [latex] T [/latex] required to transmit [latex] m [/latex] bits at a given baud rate can be calculated as:
[latex]T=frac{1}{B times n} [/latex]
6. Error Probability: In some modulation schemes, the probability of error [latex]P_e [/latex] can be related to the baud rate and noise characteristics:
[latex]P_e =f(B,Noise)[/latex]
This relationship can be complex and depends on the specific modulation scheme and noise model.
These formulas provide a mathematical framework to understand and analyze the baud rate in various contexts, from basic definitions to complex relationships with bandwidth, noise, and error probability. They are essential tools for engineers and designers working with digital communication systems.
Importance of Baud Rate in Communication Systems
- Communication Efficiency: Elevated baud rates enhance data transmission speed, fostering efficient communication between devices.
- Bandwidth Utilization: The baud rate influences the bandwidth needed for data transmission. A higher baud rate requires more bandwidth, while a lower one might lead to underutilization.
- Error Detection and Correction: Increasing the baud rate also raises the likelihood of transmission errors. Thus, a balance between speed and accuracy is vital, employing advanced error detection and correction techniques.
- Compatibility: All devices in a communication system must operate at the same baud rate to guarantee seamless data transmission. Discrepancies in baud rates can cause communication failure or data corruption.
Baud Rate in Modern Communication Systems
Modern technologies like Wifi routers and mobile phones utilize advanced modulation schemes like Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) and Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). These methods enable the transmission of multiple bits per data unit without escalating the baud rate, contributing to higher spectral efficiency and improved performance.
Conclusion
Baud rate remains a critical aspect of digital communication, governing the data transmission speed. While a higher baud rate can augment communication velocity, it must be harmonized with potential errors and channel constraints. As technological advancements continue, particularly in fields like quantum computing, the understanding and optimization of baud rate will remain vital.
Baud rate plays a crucial role in various fields, including home appliances, industrial devices, military, marine, and medical devices. Here’s an exploration of how baud rate is applied in these contexts:
Home Appliance Devices
In home appliances such as smart refrigerators, washing machines, and thermostats, the baud rate is essential for facilitating communication between different components. Modern home appliances often include touch displays that require real-time data exchange with sensors and controllers. A well-configured baud rate ensures that these devices can communicate efficiently, providing users with responsive controls and up-to-date information on the appliance’s status.
Industrial Devices
In the industrial sector, baud rate is vital for the operation of machinery and equipment that relies on precise communication between various parts. Industrial displays used in control panels must receive data from sensors and actuators at a speed that allows for real-time monitoring and control. A mismatch in baud rate can lead to delays or errors, potentially causing malfunctions or inefficiencies in the production process.
Military Applications
In military applications, the baud rate is critical for secure and reliable communication. Devices such as radar displays, communication equipment, and navigation systems must operate at specific baud rates to ensure data integrity and security. Any discrepancy in baud rate settings can lead to communication failures or interception risks, making the proper configuration of baud rate paramount in military technology.
Marine Devices
In the marine industry, navigation systems, sonar equipment, and communication devices rely heavily on the baud rate for accurate data transmission. Marine displays must receive and process data from various sensors and satellites at a speed that allows for real-time navigation and monitoring. A well-optimized baud rate ensures that marine vessels can navigate safely and efficiently, even in challenging weather conditions.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, the baud rate is integral to the functionality of devices such as patient monitors, diagnostic equipment, and medical imaging systems. These devices require a constant flow of data to provide accurate readings and visualizations. A properly configured baud rate ensures that medical professionals can rely on real-time data to make informed decisions about patient care. Any delay or error in data transmission could have serious implications for patient health and treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
The baud rate is more than just a technical specification; it’s a fundamental aspect of digital communication that impacts various fields and applications. From everyday home appliances to critical military and medical equipment, the proper understanding and configuration of baud rate are essential for the optimal performance of devices. As technology continues to evolve, the role of baud rate in ensuring efficient and reliable communication will remain a key consideration across diverse industries.
Here’s a summary of the most important information about baud rate in various contexts, presented in bullet points:
Home Appliance Devices
- Real-time Communication: Enables responsive controls and real-time status updates in smart appliances.
- User Experience: Ensures smooth interaction with touch displays in modern home devices.
Industrial Devices
- Precision Control: Facilitates precise communication between machinery components.
- Efficiency: A well-configured baud rate prevents delays or errors in production processes.
Military Applications
- Secure Communication: Critical for data integrity and security in radar, navigation, and communication systems.
- Reliability: Proper baud rate configuration prevents communication failures or interception risks.
Marine Devices
- Navigation Accuracy: Essential for real-time navigation and monitoring in marine vessels.
- Safety: Optimized baud rate ensures safe navigation, even in challenging weather conditions.
Medical Devices
- Real-time Data: Integral to patient monitors, diagnostic equipment, and medical imaging systems.
- Patient Care: Proper baud rate configuration is vital for informed decisions and patient treatment outcomes.
Conclusion
- Versatility: Baud rate is a fundamental aspect of digital communication across various fields.
- Optimal Performance: Proper understanding and configuration of baud rate are essential for the efficiency and reliability of devices in diverse industries.
The above bullet points emphasize the multifaceted role of baud rate in different sectors, highlighting its importance in ensuring effective communication, real-time data processing, security, and overall device performance.
Below is a table that outlines the most important parameters related to baud rate and their typical values in the context of displays used in home appliance devices, industrial devices, military, marine, and medical devices.
| Parameter | Home Appliance Devices | Industrial Devices | Military Devices | Marine Devices | Medical Devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Baud Rate | 9600 bps | 19200 bps | 38400 bps | 4800 bps | 115200 bps |
| Data Bits | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Parity | None | Even | Odd | None | None |
| Stop Bits | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Flow Control | None | RTS/CTS | XON/XOFF | None | RTS/CTS |
| Error Handling | Basic | Advanced | Advanced | Basic | Advanced |
| Security Considerations | Low | Medium | High | Medium | High |
Notes:
- Typical Baud Rate: The standard speed at which data is transmitted, measured in bits per second (bps).
- Data Bits: The number of bits in each character or data unit.
- Parity: Error-checking mechanism (None, Even, Odd).
- Stop Bits: The number of bits used to indicate the end of a data unit.
- Flow Control: Mechanism to control the flow of data (e.g., RTS/CTS, XON/XOFF).
- Error Handling: Level of error detection and correction (Basic, Advanced).
- Security Considerations: The level of security required in data transmission (Low, Medium, High).
These parameters and values provide an overview of the typical configurations used in different sectors. They reflect the specific requirements and considerations of each field, from the speed of data transmission to error handling and security.
Riverdi offers a diverse range of display products that cater to various applications and industries. Here’s an overview of their product catalog and how they can be relevant in different contexts:
Riverdi Product Catalog
Riverdi’s product range includes the following categories:
- STM32 Embedded Displays: These displays are suitable for embedded applications and can be found in various industrial and home appliance devices.
- RGB, LVDS, MIPI DSI LCD Displays: These versatile displays offer different connectivity options and can be used across home appliances, industrial machinery, marine navigation systems, and more.
- EVE Intelligent Displays: Designed for intelligent applications, these displays can be integrated into advanced medical devices, military equipment, and industrial control panels.
- HDMI Displays: Ideal for high-definition visual applications, these displays can be used in home entertainment systems, marine navigation, and industrial monitoring.
- E-Paper Modules: Energy-efficient and clear, E-Paper modules are suitable for various applications, including medical devices, industrial signage, and home automation.
- Evaluation Boards & Accessories: These tools facilitate the development and customization of display solutions for specific needs.
Customization Options
Riverdi also offers customization options to fit specific design, features, and functionality requirements. Utilizing high-quality materials and components, Riverdi ensures that the products meet the exact needs of the project.
Third-Party Development Tools
Riverdi supports various third-party development tools, providing an easy and efficient way to create applications. Compatible solutions include GUI building tools, development boards, and compilers, such as the EVE Screen Designer from Bridgetech and the Riverdi click from MikroElektronika.
Relevance in Different Contexts
- Home Appliance Devices: Riverdi’s touch screen options and embedded displays can enhance the user experience in smart home appliances.
- Industrial Devices: The robust and versatile displays are suitable for real-time monitoring and control in industrial settings.
- Military Applications: Intelligent and secure displays meet the high standards required for military equipment and communication systems.
- Marine Devices: High-definition and reliable displays support navigation and monitoring in marine vessels.
- Medical Devices: Riverdi’s customized and intelligent displays can be integrated into diagnostic and patient monitoring equipment, ensuring clarity and accuracy.
Conclusion
Riverdi’s extensive product catalog and customization options make them a preferred choice for various industries. From home appliances to military applications, their displays offer quality, versatility, and innovation to meet diverse requirements.
When electronic engineers are looking to design or refresh electronic devices with LCD displays, considering the baud rate is crucial for ensuring smooth communication between the device and the display. Here are some recommendations in the context of baud rate and Riverdi products:
- Understand Your Application’s Needs
- Home Appliances: For household devices like smart refrigerators or washing machines, a standard baud rate like 9600 bps might suffice. Riverdi’s STM32 Embedded Displays or RGB, LVDS, MIPI DSI LCD Displays would be suitable for such applications.
- Industrial Devices: In an industrial setting where real-time monitoring is crucial, a higher baud rate such as 19200 bps or even 38400 bps might be necessary. Consider Riverdi’s EVE Intelligent Displays for such scenarios.
- Military and Marine Devices: For applications that require high security and reliability, a well-optimized baud rate is essential. Riverdi’s HDMI Displays or EVE Intelligent Displays can be considered, ensuring that the baud rate aligns with the communication protocols of the military or marine systems.
- Medical Devices: In medical equipment where precision is paramount, a higher baud rate like 115200 bps might be beneficial. Riverdi’s E-Paper Modules or EVE Intelligent Displays would be apt choices.
- Consider Customization
- Riverdi offers customization options, allowing engineers to tailor the displays to their specific needs. Ensure that the chosen baud rate aligns with the customized features and functionalities.
- Prioritize Compatibility
- Ensure that the chosen Riverdi display is compatible with the microcontroller or processor in your device. The baud rate should be supported by both the display and the controller for seamless communication.
- Evaluate Error Handling Capabilities
- A higher baud rate might increase the chances of transmission errors. Riverdi’s products come with advanced error handling features. Ensure that these features are activated and optimized for the chosen baud rate.
- Stay Updated with Third-Party Development Tools
- Riverdi supports various third-party development tools. Familiarize yourself with these tools and ensure that they support your desired baud rate. Tools like the EVE Screen Designer from Bridgetech can be particularly useful.
- Test Extensively
- Before finalizing a design, conduct extensive testing at various baud rates to determine the optimal rate for your application. This will ensure that the display communicates effectively with the device under all conditions.
- Stay Updated with Riverdi’s Offerings
- Riverdi continuously updates its product range. Stay informed about their latest products and features, as they might offer better baud rate capabilities or other enhancements beneficial for your design.
Conclusion
Choosing the right baud rate and display product is crucial for the success of any electronic device design. Riverdi’s diverse product range and customization options provide electronic engineers with the flexibility and quality they need. By considering the above recommendations, engineers can ensure that their devices offer smooth, efficient, and reliable display communication.
The baud rate is a critical parameter in the design of displays for both home appliances and industrial devices. Here’s how designers can consider the baud rate in these contexts:
For Home Appliance Devices
- Selecting the Right Baud Rate: Choose a baud rate that balances speed and reliability. A standard rate like 9600 bps may be sufficient for most home appliances.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen baud rate is compatible with other components in the device, such as microcontrollers or sensors.
- Energy Efficiency: Consider the energy consumption related to the chosen baud rate. A higher baud rate may consume more power, so balance the need for speed with energy efficiency.
- Error Handling: Implement error detection and correction mechanisms that align with the chosen baud rate, ensuring smooth communication between the display and other components.
- User Experience: The baud rate should support real-time updates on the display, enhancing the user’s interaction with the appliance.
- Testing: Conduct extensive testing at different baud rates to find the optimal setting for your specific appliance, considering factors like noise, distance between components, and data complexity.
For Industrial Devices
- High-Speed Communication: Industrial devices often require real-time monitoring and control. Select a higher baud rate, such as 19200 bps or even 38400 bps, to support these needs.
- Robust Error Handling: Implement advanced error handling techniques that align with the chosen baud rate, ensuring reliable communication in potentially noisy industrial environments.
- Security Considerations: Consider the security implications of the chosen baud rate. A well-configured baud rate can enhance the security of data transmission within the industrial system.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Ensure that the chosen baud rate is compatible with existing industrial control systems and communication protocols.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the system when selecting the baud rate. It should support future expansions or modifications without requiring significant changes to the communication settings.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the chosen baud rate complies with relevant industrial standards and regulations, maintaining the integrity and safety of the system.
Conclusion
The baud rate is a fundamental aspect of designing displays for both home appliances and industrial devices. It influences the speed, reliability, efficiency, and security of communication within the system. By carefully selecting and configuring the baud rate, designers can create devices that not only meet functional requirements but also offer robust performance in various environments. Whether it’s a simple home appliance or a complex industrial machine, the right baud rate setting is key to successful communication and overall device performance.
Summary
Here’s a summary of the key considerations and recommendations for designing displays in home appliances and industrial devices, with a specific focus on the baud rate:
Home Appliance Devices:
- Baud Rate Selection: A standard rate like 9600 bps may suffice, balancing speed and reliability.
- Compatibility: Ensure alignment with other components like microcontrollers or sensors.
- Energy Efficiency: Consider power consumption related to the chosen baud rate.
- Error Handling: Implement mechanisms that align with the baud rate for smooth communication.
- User Experience: Support real-time updates on the display to enhance user interaction.
- Testing: Conduct tests at different baud rates to find the optimal setting.
Industrial Devices:
- High-Speed Communication: Select a higher baud rate (e.g., 19200 or 38400 bps) for real-time monitoring and control.
- Robust Error Handling: Implement advanced techniques for reliable communication in industrial environments.
- Security Considerations: Enhance data transmission security through well-configured baud rate settings.
- Integration: Ensure compatibility with existing industrial control systems and protocols.
- Scalability: Choose a baud rate that supports future expansions or modifications.
- Compliance: Adhere to relevant industrial standards and regulations.
Conclusion:
The baud rate plays a vital role in the design of displays for both home appliances and industrial devices. It’s a key factor that influences communication speed, reliability, efficiency, and security within the system. Careful selection, configuration, and testing of the baud rate can lead to successful communication and robust performance in various environments. Whether for simple home use or complex industrial applications, the right baud rate setting is essential for optimal device functionality and user satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ
Q1: What is the baud rate, and why is it important?
A1: The baud rate is the speed at which data is transmitted between devices, measured in symbols per second. It’s crucial for ensuring smooth communication between components like displays and microcontrollers, affecting speed, reliability, and efficiency.
Q2: What is a typical baud rate for home appliance devices?
A2: A standard baud rate like 9600 bps (bits per second) is often sufficient for home appliances, balancing communication speed with energy efficiency and reliability.
Q3: How do I choose the right baud rate for industrial devices?
A3: Industrial devices may require higher baud rates, such as 19200 or 38400 bps, for real-time monitoring and control. Consider factors like error handling, security, integration, scalability, and compliance with standards.
Q4: How does the baud rate affect energy consumption?
A4: Higher baud rates may consume more power, so it’s essential to balance the need for speed with energy efficiency, especially in battery-operated or always-on devices.
Q5: How can I ensure compatibility with the chosen baud rate?
A5: Compatibility can be ensured by selecting a baud rate that aligns with other components in the system, such as microcontrollers, sensors, and communication protocols. Testing and validation are also vital.
Q6: What are the security considerations related to baud rate?
A6: A well-configured baud rate can enhance data transmission security, especially in industrial settings. Implementing proper error handling and adhering to relevant standards can further improve security.
Q7: How does the baud rate affect user experience in home appliances?
A7: The baud rate should support real-time updates on the display, enhancing user interaction and responsiveness in home appliances like smart refrigerators or thermostats.
Q8: Can I change the baud rate after designing the device?
A8: While it’s possible to change the baud rate, it may require adjustments to other components and settings. It’s best to determine the optimal baud rate during the design phase to avoid potential issues later.
Q9: How do I test the optimal baud rate for my device?
A9: Conduct extensive testing at different baud rates under various conditions, considering factors like noise, distance between components, and data complexity. Simulation tools and real-world testing can help find the optimal setting.
Conclusion:
The baud rate is a fundamental aspect of designing displays for home appliances and industrial devices. Understanding its implications on speed, reliability, efficiency, and security is key to creating successful products. This FAQ provides insights into common questions and considerations related to baud rate, aiding designers in making informed decisions.
DISCOVER OUR
Whitepaper
Achieve the perfect user-display interaction with the right Touch Sensor IC. Ever faced issues with phantom touch events or certification? Boost your R&D like a pro with our Whitepaper!