- Understanding Header Pins: Importance and Applications in Industrial Displays
- What Are Header Pins?
- Key Benefits of Using Header Pins
- Example Applications of Header Pins
- Header Pin Dimensions and Sizes
- Male vs. Female Header Pins
- Connecting Pin Headers on PCBs
- Key Applications of Header Pins in Industrial Displays
- Riverdi Product Catalog Overview
- Key Specification Considerations for Industrial Applications
- Integrating Header Pins into HMI and Panel Design
- Key Takeaways on Header Pins for Industrial Applications
- Header Pins in Home Appliances & Industrial Devices: FAQ
- Q1: Why are header pins important in electronic device design?
- Q2: How do I choose the right header pin for industrial environments?
- Q3: Are header pins safe for home appliances, especially those exposed to water?
- Q4: How do header pins facilitate easier maintenance and upgrades?
- Q5: What should I consider regarding space when designing with header pins?
- Q6: How can I ensure secure connections in vibration-prone environments?
- Q7: Why is standardization of header pin configurations recommended?
- Q8: How crucial is documentation when designing with header pins?
- Q9: Should I test header pin connections before finalizing my design?
- Q10: Are there specific header pins for different applications like home vs. industrial?
Understanding Header Pins: Importance and Applications in Industrial Displays
Header pins are an essential component in connecting circuit boards and wiring in industrial grade displays and electronic devices. As we move towards smarter and more connected technology across industries, understanding the role of header pins is key for engineers, project managers and purchasing specialists selecting the right components.
This guide will provide a comprehensive look at what header pins are, connecting pins, header pin dimensions and pin header sizes, male to female headers, what is a header board for prototyping, and most importantly, their varying applications across industrial displays, HMIs, POS systems, retail displays, smart devices, IoT, EVs, medical devices, military equipment, marine electronics, home appliances, and more.
What Are Header Pins?
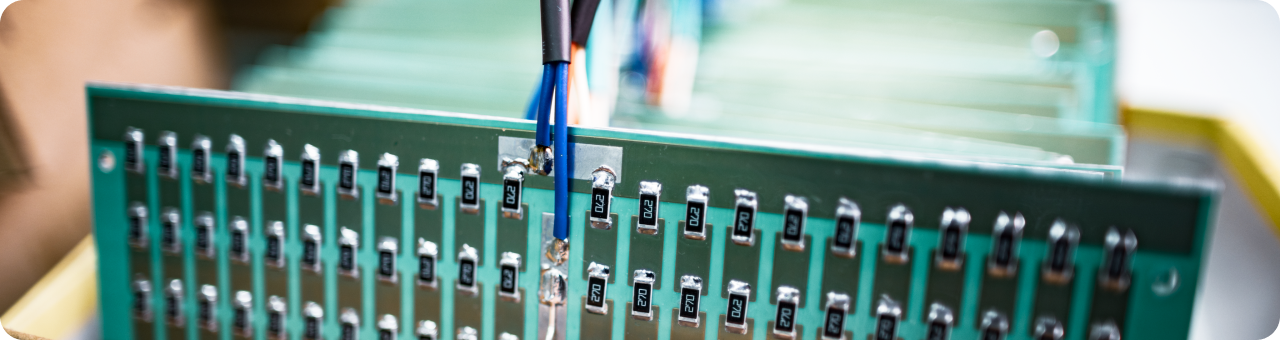
Header pins, also referred to as connector pins or header connectors, are short pins or terminals that are inserted into holes in circuit boards to allow connection of wires and cables. They provide both mechanical and electrical connections between boards, cables, and components.
The pins are arranged in parallel rows embedded in plastic or nylon housing to form a header. The spacing between the pins enables a matching socket or other header to mate with the arrangement of pins, creating a removable connection.
Header pins serve as an interface for connecting external wiring and components to printed circuit boards (PCB). They are integrated into boards through pin headers soldered on. Wires can then be crimped or soldered to the back of the header pins.
Key Benefits of Using Header Pins
Header pins offer several important benefits that make them a staple in electronics:
- Removable connections Headers allow for components to be easily attached and detached from a PCB without desoldering. This enables modifications, replacements, and changes.
- Flexibility A wide range of header styles are available to accommodate various connectivity needs. Pin count, pitch, height, and other factors can be specified.
- Reliability Industrial grade header pins are designed for dependability and durability in demanding environments. Proper mating helps prevent disconnected wires.
- Versatility Header pins have broad applications for connecting peripheral devices, wiring, cables, boards, and more. Standard interfaces enable versatility.
- Serviceability Wires and cables can be changed out or serviced without altering soldered connections on boards. This helps maintenance and repairs.
- Cost-effectiveness Header connectors provide a budget-friendly interface option compared to costly custom connectors. They are widely available and reusable.
Header pins enable optimized connectivity, interchangeability, and longevity across electronics and devices. Their flexibility and simplicity make them a foundational wiring method.
Example Applications of Header Pins
Prototyping Boards
One of the most common uses of header pins is on prototypes. They allow for quick and temporary connections, ideal for testing circuit designs.
Arduino and Raspberry Pi
These popular microcontroller and microcomputer platforms utilize header pins for connecting to sensors, actuators, and other modules.
Shield & HAT Boards
Many extension boards, known as shields (for Arduino) or HATs (for Raspberry Pi), use header pins to stack on top of the main board, expanding its capabilities.
JTAG and ISP Programming
Header pins are used for Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) and In-System Programming (ISP) interfaces, allowing developers to program or debug microcontrollers and FPGAs.
PC Motherboards
Header pins on motherboards provide connections for front panel controls, USB ports, and other peripherals.
Modular Electronics
In modular electronics, where components can be added or removed based on requirements, header pins provide the necessary connectivity.
Header pins, with their simplicity and efficiency, have become an integral part of modern electronics. They not only provide flexibility in design but also streamline the testing and development process. Whether you’re a hobbyist building a DIY project or a professional designing a complex electronic system, understanding the importance and applications of header pins is crucial.
Header Pin Dimensions and Sizes
To select the right header pins for an application, engineers need to understand common dimensions and specifications. Key factors include:
Number of Pins
Header connectors are available in a wide range of pin counts, typically from 2 pins up to 100 pins. Higher density headers packing more pins in compact footprints are also produced. Popular pin numbers include 2, 3, 4, 6, 10, 20, 40, and 50.
The needed pin count depends on the number of interconnections needed. More pins supply flexibility for more wiring terminations.
Pitch or Spacing
Pitch is the distance between pin centers, measured in mm. Standard pitches range from 1.27mm to 2.54mm. High density headers have pitches of 1mm or less. Pitch must match between headers and mating connectors.
Common pitches include:
- 2.54mm – The most popular standard pitch
- 2mm
- 1.27mm
- 1mm or less
Narrower pitches allow more pins in smaller footprints, while wider pitches provide more space for traces and vias on boards.
Pin Lengths
Pin length, measured in mm, determines how far the pins extend from the connector housing. Usual pin lengths range from ~2mm to 12.7mm, but longer versions are available. The ideal length depends on board thickness and component spacing.
Longer pins provide more flexibility for varying board and component heights. Shorter pins take up less space. Right-angle options are also available.
Row Spacing
For headers with multiple rows, the row spacing or pitch determines the distance between rows. Typical row spacing is 7.62mm or 5.08mm. Row spacing must match the component or socket being connected.
Pin Diameter
Pin diameter is 0.36mm to 0.64mm. Larger diameters add durability. Smaller pins work for high density applications. Diameter affects current carrying capacity.
Housing Material and Style
Headers come in nylon, plastic, or fiberglass housings. Key housing choices include:
- Single vs. dual row
- Straight or right angle
- Surface mount or through-hole mount
- Shrouded or unshrouded
Housing selection depends on space, board mount type, and insertion/removal needs.
Male vs. Female Header Pins
Header pins are designed in male and female versions, with pins configured to mate with corresponding sockets and connectors.
Male Header Pins
Male header pins consist of pins protruding from a plastic housing in a parallel array. The protruding pins are inserted into female sockets or connectors. Solder tabs or wire clips may be present on the back for termination.
Male headers extend connectivity from a board or component. They plug into female receptacles on mating connectors and sockets. This arrangement provides a detachable interface.
Male headers are often integrated on circuit boards through soldered pin header connectors. Wiring can then be extended via the protruding pins.
Female Header Sockets
Female header connectors contain parallel sockets designed to receive male header pins. The female sockets form recessed holes within a plastic housing. Wiring terminates into the back side.
The female sockets align with and connect to the pattern of pins on a mating male header. This provides a detachable plug-and-socket connection between components and wires.
Female headers enable external wiring to be joined to male pin interfaces in a removable way. They are commonly integrated into cable assemblies.
Connecting Pin Headers on PCBs
Pin headers designed for soldering provide an effective method of integrating detachable connections into printed circuit boards.
The process involves:
- Soldering pin header connector onto circuit board. The plastic housing sits flush on the PCB.
- Soldering individual pins to copper pads/traces on the board establishes mechanical and electrical connection.
- Pins extend out the opposite side of the board with plastic header housing on surface.
- External wiring interfaces with the protruding pins to extend connections off board.
- Complementary female socket connectors mate with pins to complete the interface.
Proper soldering of pin header footprints locks the header in place securely while maintaining connection integrity under mating cycles.
Board-mount headers can be placed anywhere needed on the PCB layout. They allow flexibility in locations of detachable wiring interfaces. Vertical headers take up minimal space.
Right-angle headers lying parallel to the board surface are also available. These provide a more low-profile option.
Key Applications of Header Pins in Industrial Displays
Now that we have covered the basics of header connector designs and dimensions, let us look at some of the key applications and benefits of using header pins in industrial display interfaces.
HMI and Panel Mount Displays
Human-machine interface (HMI) panels with integrated displays often use header connectors to link to:
- Touchscreen controllers Display-integrated touchscreen sensors route through header pin connections to controller boards. This allows interchangeability.
- Backlight drivers LED backlight power and controls route through header connectors from driver boards to displays.
- Power Terminals Header pin power terminals enable easy connection of power from external sources to power boards.
- Control Inputs External controls like switches route into displays via header connectors.
- Communications Data cables joining to COM ports use header pin connections for transmission in and out of an HMI display.
Removable cabling through header pin interfaces enables simplified servicing and replacement of HMI components.
POS and Kiosk Displays
Point of sale (POS) systems and interactive kiosks depend on header connectors for:
- Joining peripherals like barcode scanners, cash drawers, card readers, receipt printers, etc.
- Connecting touchscreen overlay components.
- Extending connections for power, video, and data to the main display/PC.
- Linking small interconnect boards back to the main circuit assembly.
Being able to easily detach cables and components makes service and upgrades more straightforward for POS/kiosk systems.
Digital Signage and Video Walls
Video walls, menu boards, and digital signage use header pin connections to:
- Link individual panels together into video wall configurations.
- Connect external media players, video controllers, cameras.
- Join peripherals like touch overlays, sensors, payment terminals, etc.
- Extend power and data connections.
Easily swapping components in and out helps enable flexible digital signage arrangements.
Retail and Restaurant Displays
In retail locations, header connectors are key for:
Connecting peripherals like barcode/QR code scanners, card readers, scales, etc.
- Linking self-service kiosks and price checkers.
- Joining components of smart shelves, smart mirrors, and interactive displays.
- Integrating lighting controls, sensors, security devices.
- Providing standardized power and data termination points.
Being able to modify connections simplifies upgrades and maintenance for constantly evolving store technology.
Medical and Laboratory Displays
In medical devices and lab equipment, headers provide:
- Sensor/probe connectivity into analysis instruments.
- Touchscreen and user interface connections.
- Video routing from endoscopes/cameras to displays.
- Integration of analytical modules and additional hardware.
Swap-ability of components is crucial for adjusting medical/lab gear and keeping it updated.
Military and Marine Electronics
Rugged displays used in defense, aerospace, and marine settings depend on header pins to enable:
- Quick replacement of damaged display modules in the field.
- Integration of varying modules like radios, tactical interfaces, GPS, etc.
- Connecting peripherals and lights via standard interfaces.
- Reliable power input connections.
Being able to rapidly reconfigure mission-critical systems under harsh conditions is essential.
Test and Measurement Equipment
For industrial test and measurement systems, headers provide:
- Sensor connections from measurement probes.
- Inputs for signals being analyzed.
- Video outputs to integrated displays.
- Links between stacked circuit boards.
- Connections to data recorders and analyzers.
Headers enable extensive connectivity in complex measurement electronics.
Industrial Control and Automation
Header pins used in industrial automation systems connect:
- Inputs and outputs to/from PLCs and controllers.
- HMIs and their integrated touch panels.
- System components like drives, power supplies, safety controls, sensors, etc.
- External circuits for power, controls, management, etc.
Removable connections aid troubleshooting and replacement of components in automation systems.
Smart Home Devices
Even in smart home devices and appliances, you will see headers used for:
- Connecting integrated touchscreen panels.
- Linking components like control boards, sensors, Wi-Fi modules.
- Providing serviceability access to internal electronics.
- Power and data ingress/egress.
Header pin usage spans the spectrum from complex industrial equipment down to consumer smart home tech.
Here a table with the most important parameters and their typical values in context of header pins importancy in home appliance devices, industrial devices, military, marine and medical devices.
Parameter | Home Appliance Devices | Industrial Devices | Military Applications | Marine Devices | Medical Devices |
Material | Brass, Tin-plated | Gold-plated, Brass | Gold-plated, Nickel | Corrosion-resistant alloys | Gold-plated, Nickel |
Pin Count | 2-20 pins | 2-50 pins | 2-100 pins | 2-40 pins | 2-50 pins |
Current Rating | 1-3A | 2-5A | 3-5A | 2-4A | 1-3A |
Voltage Rating | 50-250V | 60-400V | 50-300V | 50-250V | 50-300V |
Temperature Range | -10°C to 85°C | -40°C to 125°C | -55°C to 125°C | -20°C to 85°C | -10°C to 100°C |
Durability (Insertions) | 500-1,000 | 1,000-10,000 | 10,000-20,000 | 1,000-5,000 | 500-5,000 |
Connector Type | Male/Female | Male/Female/Shrouded | Male/Female/Shrouded | Male/Female | Male/Female/Shrouded |
Pitch (Distance between pins) | 2.54mm (common) | 2mm-2.54mm | 1.27mm-2.54mm | 2.54mm | 1.27mm-2.54mm |
Note: The values provided in the table are typical and can vary based on specific requirements and manufacturers. Always refer to the datasheet or manufacturer’s specifications for precise values.
Riverdi Product Catalog Overview
Riverdi offers a diverse range of products tailored to meet various project requirements. Here’s a snapshot of their offerings:
- Touch Screen Options: Riverdi provides uxTouch, capacitive, and resistive touch screen options.
- Screen Sizes: They offer a range of screen sizes, from 3.5″ to 10.1″.
- Graphics Controllers: Various graphics controllers are available to choose from.
Product Categories
- STM32 Embedded Displays: These are displays integrated with STM32 microcontrollers.
- RGB, LVDS, MIPI DSI LCD Displays: Different types of LCD displays with various interfaces.
- EVE Intelligent Displays: Advanced displays with integrated graphics processing.
- HDMI Displays: Displays with HDMI interface.
- E-Paper Modules: Electronic paper display modules.
- Evaluation Boards: Boards designed for testing and evaluation purposes.
- Accessories: Additional components and tools to complement the displays, like Riverdi ZIF Connectors.
Customization Options
Riverdi emphasizes customization, ensuring products meet specific design and functionality requirements. They utilize high-quality materials and components, combined with their team’s expertise, to deliver tailor-made solutions.
Third-Party Development Tools
Riverdi supports a variety of third-party tools to facilitate the development process. This includes GUI building tools, development boards, compilers, and more. Notable mentions include the EVE Screen Designer from Bridgetech and the Riverdi click from MikroElektronika.
Key Specification Considerations for Industrial Applications
Engineers selecting header pins for displays and electronics in demanding industrial settings should keep these specifications in mind:
Durability
Look for headers in high-temp, reinforced plastics or metal housings that withstand vibration, shock, moisture, and repeated mating cycles.
Contact Plating
Pins plated in gold, tin, or nickel resist corrosion and ensure consistently low contact resistance for reliable connectivity.
Pitch Spacing
Choose pitch based on board layouts, housing sizes, and mating components. May require high-density <2mm pitch.
Current Rating
Ensure current capacity meets power needs. Larger 0.64+mm pins help conduct more current.
Insulation
Well-insulated housings prevent shorts between contacts. Metallic housings offer robust shielding.
Keying
Keyed headers that only mate to matching connectors prevent misconnections.
Latching
Positive latching mechanisms like clips help avoid loose connections from vibration/shock.
Environmental Sealing
Sealed connections maintain performance despite moisture, debris, temperature extremes.
Integrating Header Pins into HMI and Panel Design
Carefully planning integration of header connectors into your HMI panel and electronics designs ensures optimal connectivity and performance. Keep these guidelines in mind:
- Define requirements Determine how wiring needs to interface based on hardware architecture and use environment. This drives pin count, pitch, spacing, etc.
- Layout footprint Develop board footprints and 3D models with header pins in placement needed for access and clearance.
- Select hardware Choose header connectors and matching sockets that align with requirements. Seek help from specialists if needed.
- Review drawings Verify header connector locations and alignments in panel design drawings before production.
- Mind assembly Follow manufacturer instructions carefully when assembling and soldering header pins onto boards.
- Test connections Functionally evaluate boards and components with mated headers to validate proper connectivity.
- Plan access Design housing, doors, plates, etc. to allow convenient access to header connectors for wiring.
- Document interfaces Thoroughly document header pin connections in diagrams and manuals to assist installers and service technicians.
Taking considerations like these into account helps you effectively harness the flexibility and serviceability of header pin connections in your industrial displays and systems.
Key Takeaways on Header Pins for Industrial Applications
Header pin connectors serve as the attachment points connecting PCBs with vital external wiring in industrial electronics. Their ability to enable removable, configurable connections makes them indispensable:
- A wide range of headers are available to suit connectivity needs via standard interfaces.
- Dimensional factors like pin count, pitch, length, and spacing must be matched between headers and mating components.
- Male pins protruding from housings plug into female socket connectors to form detachable junctions.
- Headers efficiently integrate removable wiring connections directly onto circuit boards.
- From HMIs to test equipment to automation systems, headers simplify servicing of industrial electronics.
- For demanding environments, ruggedized metal or high temperature plastic housings provide durable performance.
Understanding header pin selection, integration, and best practices empowers design engineers to implement optimized connectivity architectures. As industries continue the drive towards smarter and more interconnected technologies, leveraging the flexibility of header connectors is an essential skill for project and purchasing specialists alike.
In essence, when incorporating header pins into device designs, it’s crucial to prioritize reliability, safety, and adaptability. Proper planning and testing can lead to efficient, user-friendly, and maintainable devices.
Header Pins in Home Appliances & Industrial Devices: FAQ
Q1: Why are header pins important in electronic device design?
A: Header pins offer modularity, allowing for easy assembly, disassembly, and upgrades. They also simplify maintenance by enabling quick component replacements without soldering.
Q2: How do I choose the right header pin for industrial environments?
A: For harsh industrial conditions, opt for corrosion-resistant header pins that can withstand factors like temperature fluctuations, humidity, and dust.
Q3: Are header pins safe for home appliances, especially those exposed to water?
A: Yes, but it’s essential to ensure that the header pins and connectors are insulated or positioned to prevent accidental short circuits. Always consider the typical environment of the appliance.
Q4: How do header pins facilitate easier maintenance and upgrades?
A: Header pins allow for the easy replacement of modules. This means if a component fails or needs an upgrade, only that specific module can be swapped out without affecting the entire system.
Q5: What should I consider regarding space when designing with header pins?
A: While header pins offer flexibility, they also occupy space. Designers should account for their space requirements to ensure the device maintains its desired form factor.
Q6: How can I ensure secure connections in vibration-prone environments?
A: In settings with vibrations, like industrial sites, consider using locking connectors or shrouded headers to prevent accidental disconnections.
Q7: Why is standardization of header pin configurations recommended?
A: Standardizing pin configurations across devices simplifies maintenance, reduces inventory complexity, and ensures consistency, making it easier for technicians to service devices.
Q8: How crucial is documentation when designing with header pins?
A: Extremely crucial. Clear documentation on pin configurations, functions, and standards aids in troubleshooting and ensures design and manufacturing consistency.
Q9: Should I test header pin connections before finalizing my design?
A: Absolutely. It’s essential to prototype and test header pin connections under various conditions to ensure they meet required standards and real-world scenarios.
Q10: Are there specific header pins for different applications like home vs. industrial?
A: While the fundamental design might be similar, header pins for industrial applications might be more robust and corrosion-resistant compared to those for home appliances.
DISCOVER OUR
Whitepaper
Achieve the perfect user-display interaction with the right Touch Sensor IC. Ever faced issues with phantom touch events or certification? Boost your R&D like a pro with our Whitepaper!