Screen Rotation
This manual provides clear, step-by-step instructions on how to rotate the display screen in Riverdi HDMI modules. Screen rotation is often required to adjust the display orientation for vertical or inverted installations, ensuring proper image alignment and usability. Whether you are configuring a Riverdi display for digital signage, a touchscreen interface, or an embedded system, this guide will help you set the correct screen orientation quickly and accurately.
OSD Menu Rotation
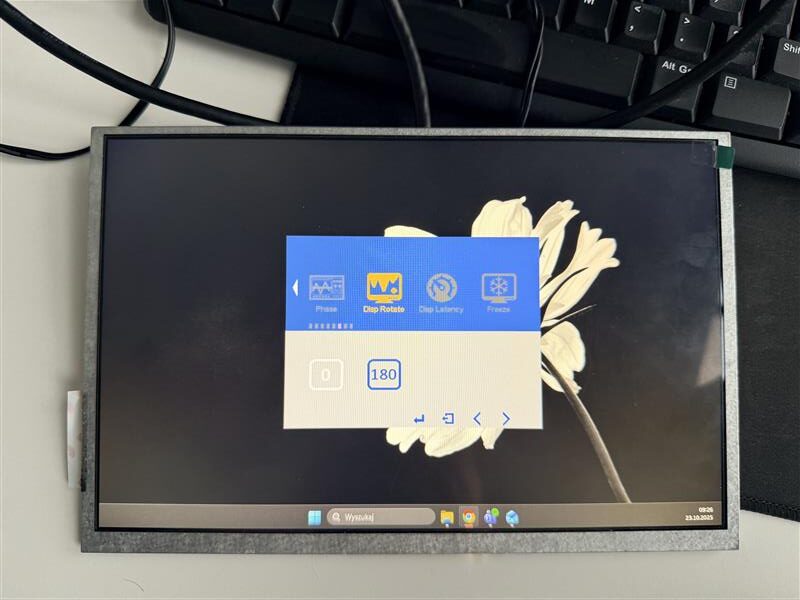
Screen rotation in Riverdi HDMI modules can be performed directly through the display’s On-Screen Display (OSD) menu. However, it is important to note that this method is recommended only for 180-degree rotation and for modules without a touch panel. Using the OSD rotation on touch-enabled modules may cause the touch coordinates to become misaligned with the displayed image.

Screen orientation normal(OSD)


Screen orientation 180 degrees(OSD)
Windows OS Screen Rotation
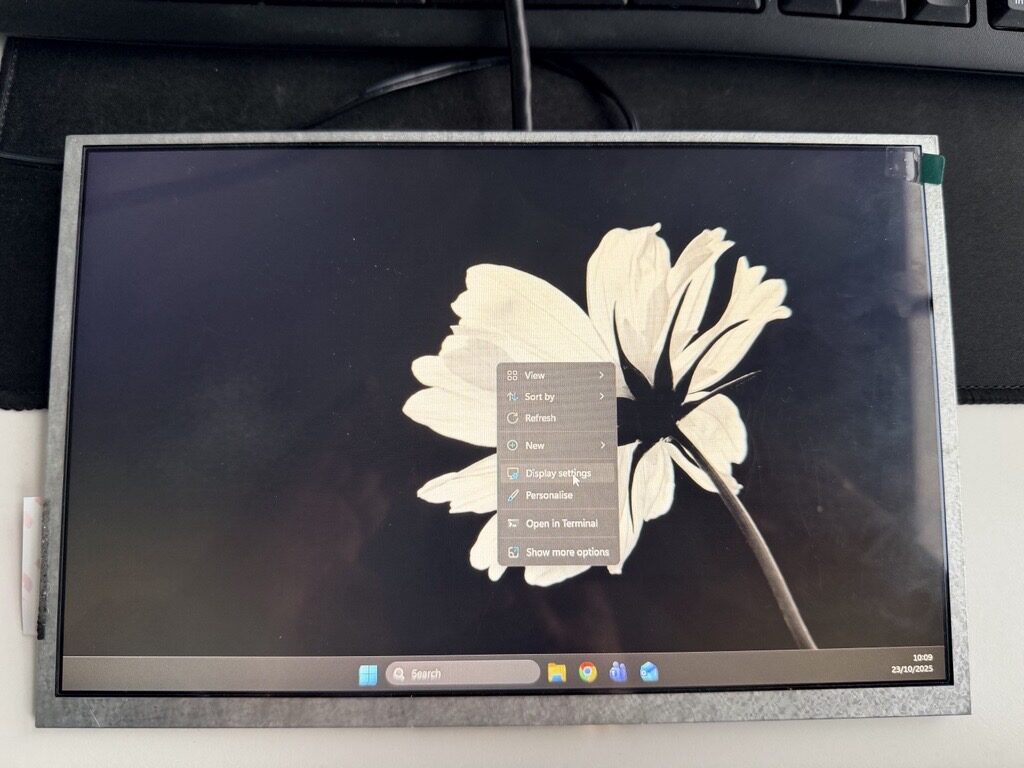
When using Riverdi HDMI modules with a touch panel, screen rotation should be performed directly in the Windows operating system. This approach ensures that both the display image and the touch coordinates remain correctly aligned without the need for additional calibration. The orientation can be easily changed in the Display Settings by selecting the appropriate mode, such as normal or flipped (180°) orientation.

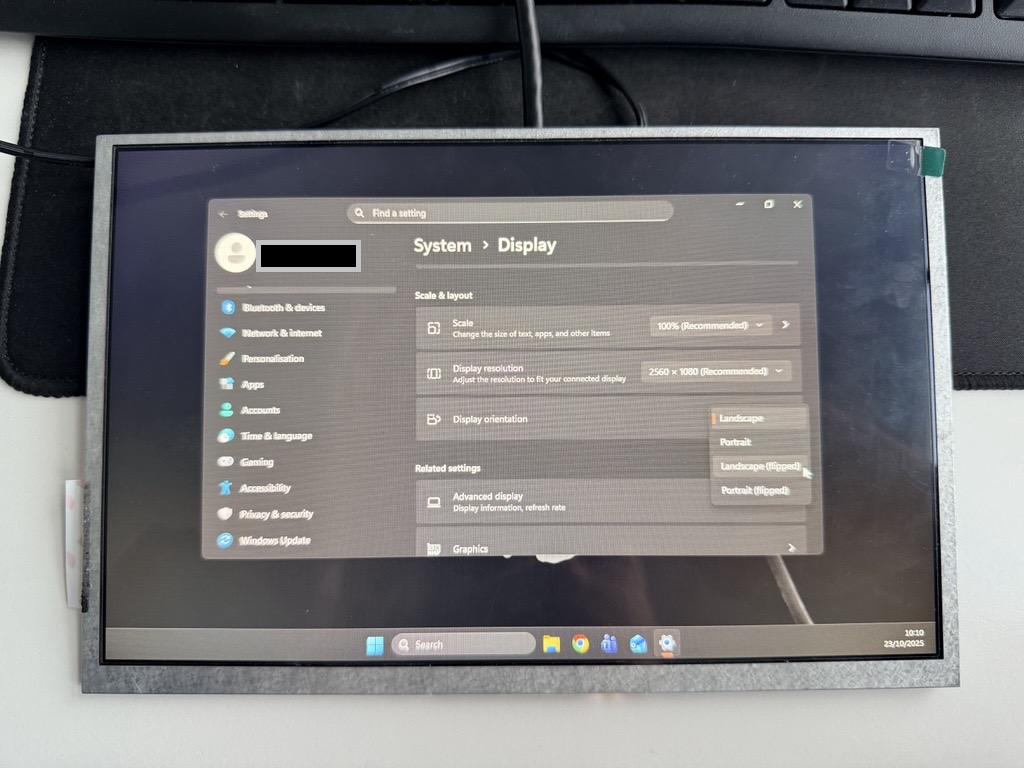



Linux OS Screen Rotation
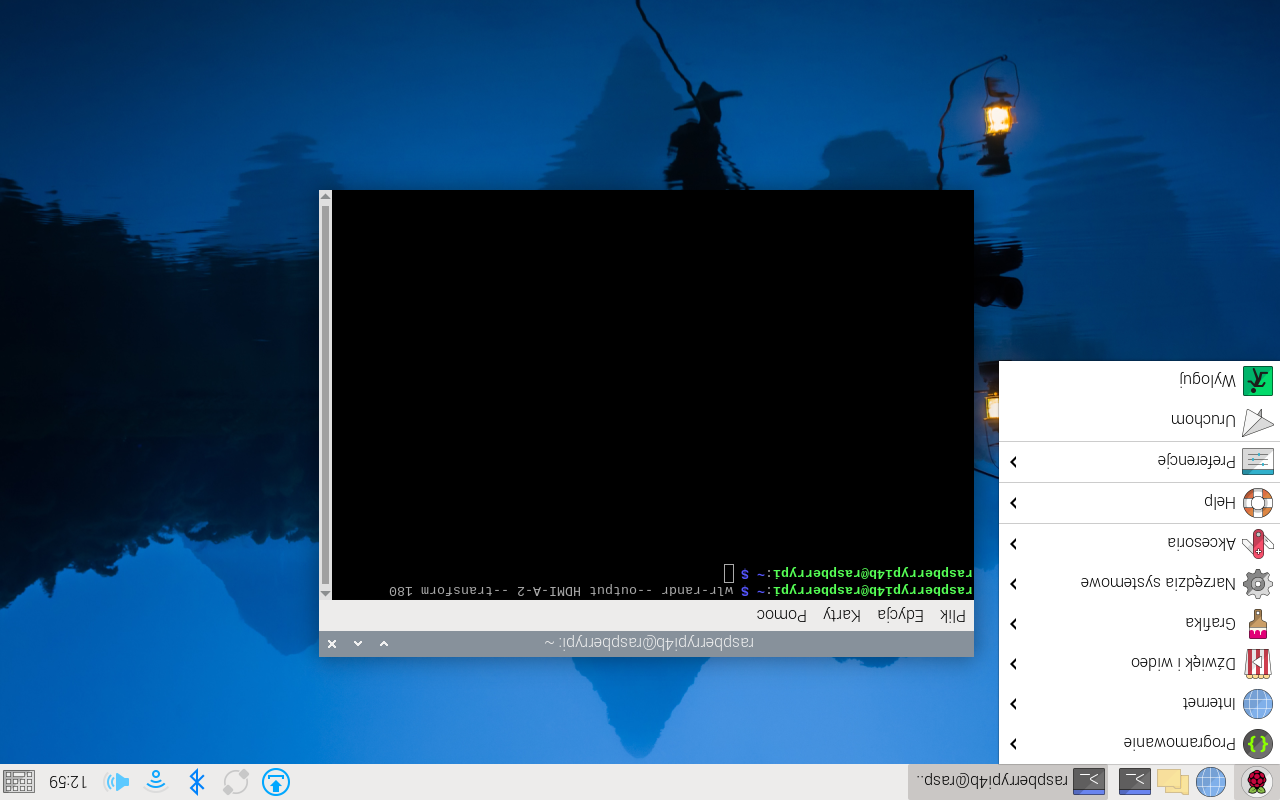
In Linux systems, screen rotation for Riverdi HDMI modules can be configured using display management tools such as xrandr or wlr-randr. These utilities allow you to set the desired screen orientation — normal, inverted, left, or right — either through the command line or system display settings.
When using a module with a touch panel, it is necessary to ensure that the touch coordinates are correctly mapped after rotation. To achieve this, appropriate configuration entries should be added to the system configuration file.
In X11-based systems, this can be done in the /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/ directory, while in Wayland-based environments such as Labwc, the configuration should be added to the ~/.config/labwc/inputs file. There, you can define both the display mapping and rotation for the touch device.
Skipping part when the version of Linux OS is known.
Below example shows how to modify the display settings on Linux Debian 12(bookworm).
Before moving on with screen rotation.
Install wayland protocols
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y git meson ninja-build pkg-config build-essential wayland-protocols libwayland-dev libxkbcommon-dev
Check name of screen
wlr-randr
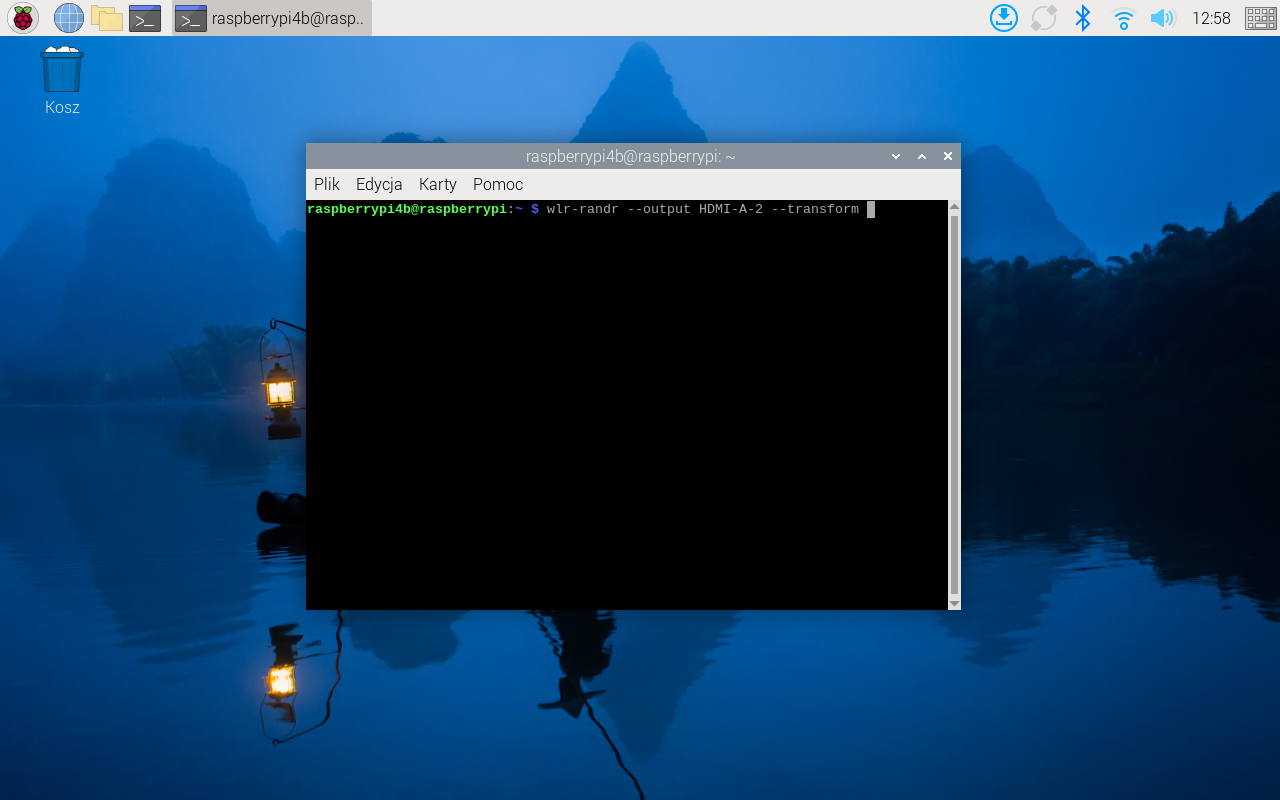
Commands to rotate screen:
wlr-randr –output (name of the device) –transform 90
wlr-randr –output (name of the device) –transform 270
wlr-randr –output (name of the device) –transform 180
wlr-randr –output (name of the device) –transform normal
Check what is the Touch Input
libinput list-devices
In the example it is:
Device: ILITEK ILITEK-TOUCH
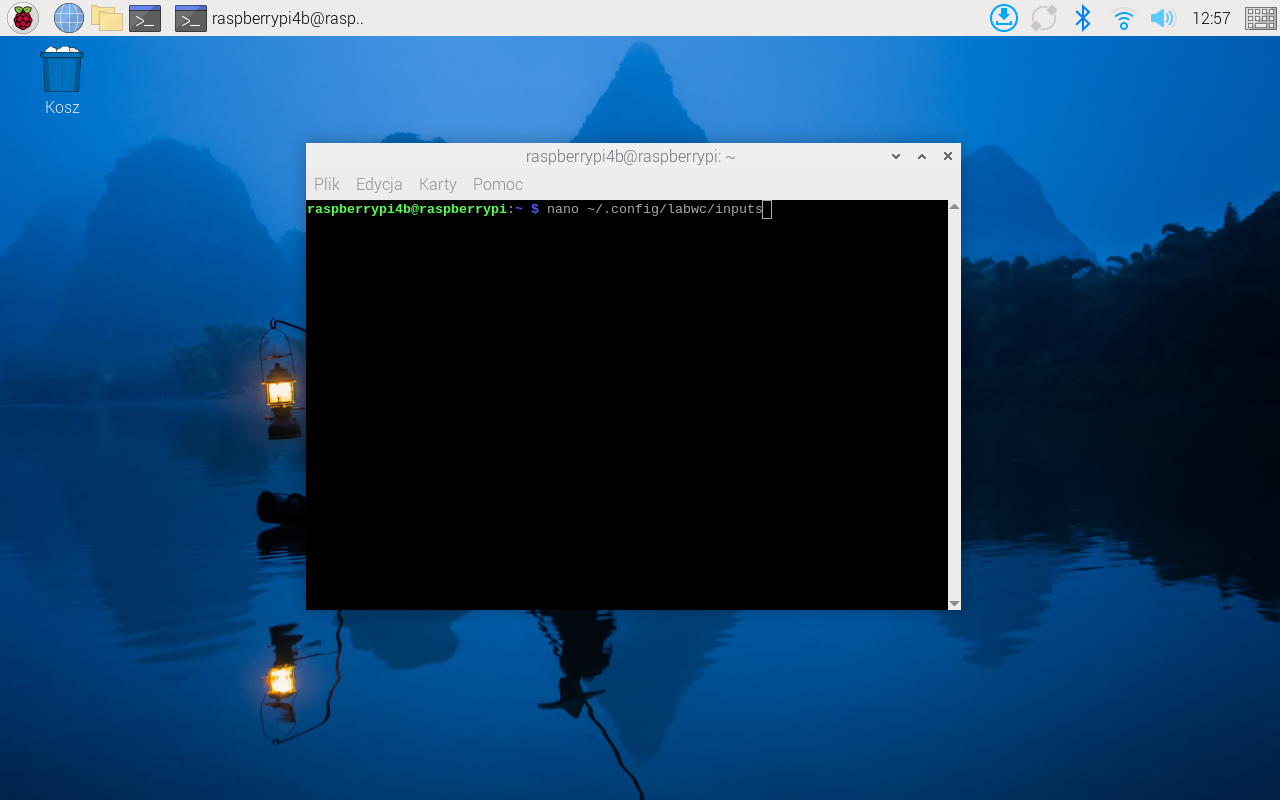
Open confing file
nano ~/.config/labwc/inputs
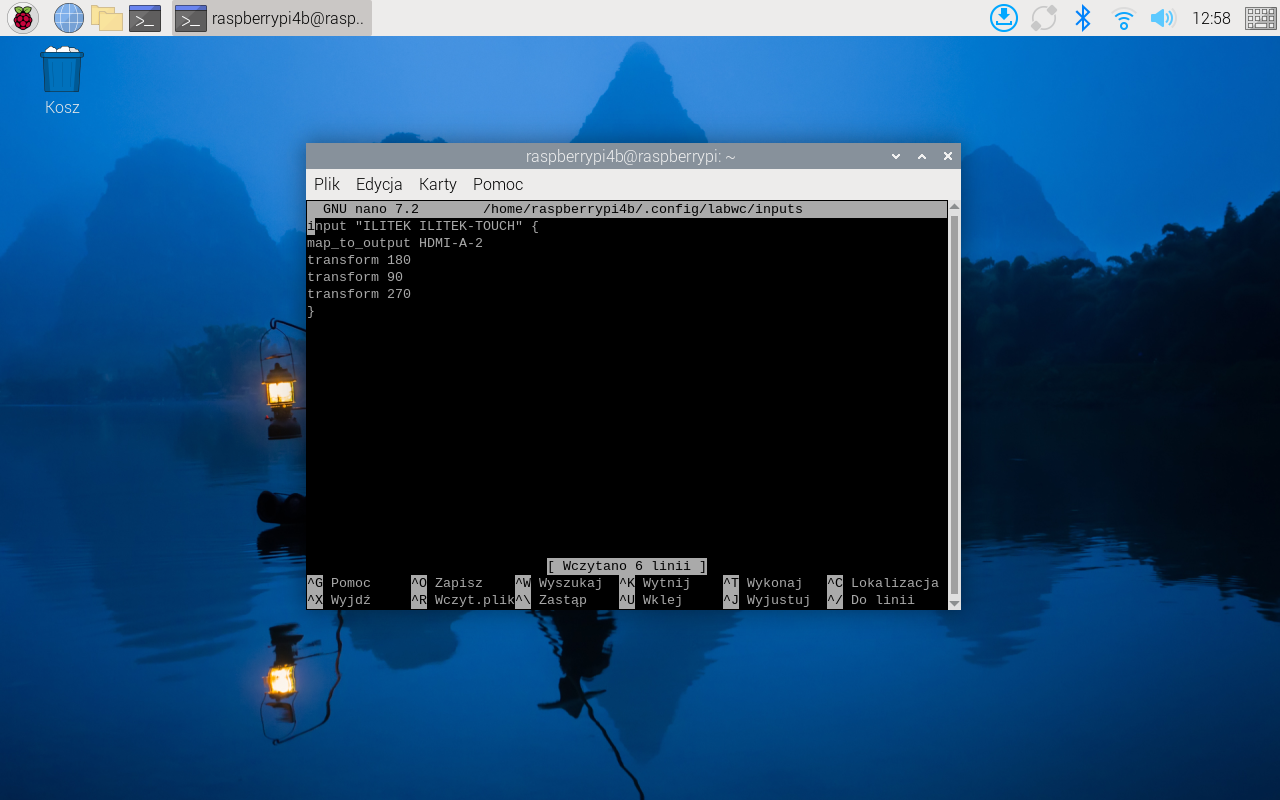
Make this setting, it maps the Touch for the rotation of the screen.
input “ILITEK ILITEK-TOUCH” {
map_to_output HDMI-A-2
transform 180
}
In the last part whene editing config file. User can add also other rotations, like shown on the picture below.
Note that this setting is temporary. After reset it will get back to normal.
Both of the above described methods where tested on all of the HDMI modules sold by Riverdi.
5″, 7″, 10″, 12.1″, 15″.
DISCOVER OUR
Whitepaper
Achieve the perfect user-display interaction with the right Touch Sensor IC. Ever faced issues with phantom touch events or certification? Boost your R&D like a pro with our Whitepaper!